Banking & Insurance Awareness
Banking & Insurance Awareness

What is Banking Awareness? Banking awareness means complete knowledge of banks and what is going on in banking sector. In other words get completely updated knowledge of the banking policies and schemes in order to get the full benefit
History of Banking in India: Banking in India, in the modern sense, originated in the last decades of the 18th century. Among the first banks were the Bank of Hindustan, which was established in 1770 and liquidated in 1829–32; and the General Bank of India, established in 1786 but failed in 1791
The largest bank, and the oldest still in existence, is the State Bank of India (S.B.I). It originated as the Bank of Calcutta in June 1806. In 1809, it was renamed as the Bank of Bengal. This was one of the three banks funded by a presidency government.
For many years the presidency banks had acted as quasi-central banks, as did their successors, until the Reserve Bank of India was established in 1935, under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
Structure of Banking in India:
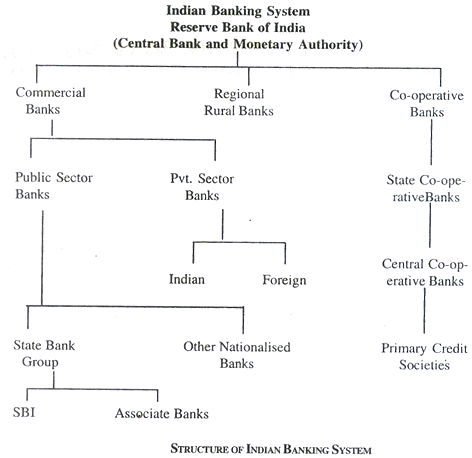
Difference between Scheduled and non-scheduled banks; Different types of Scheduled Commercial Banks; State Bank of India, Private Banks, Old private banks and new private banks, Foreign Banks in India, Share of Foreign Banks in Banking Business; RBI policy towards Foreign Banks in India; Regional Rural Banks ; Cooperative Banking.
Types of Banking: Basic Information about various types of Banking in India and elsewhere. We may now make a brief review of different types of banks in India.
Commercial banks: Commercial banks are the most important types of banks. The term ‘commercial’ carries the significance that banking is a business like any other business. In other words, commercial banks are essentially profit-making institutions. …
Development banks: Development banks are parts of a country’s capital market. In India they are called public financial institutions. They are specialized financial institutions which supply long-term finance to large and medium industries. …
Co-operative banks: The co-operative banks are set up under the provisions of the co-operative society’s laws of a country. In India such banks have been set up to provide credit to primary agricultural credit societies at low rates of interest. However, some co-operative banks also function in rural areas….
Land development banks: : These banks (called land mortgage banks in India) provide long-term credit to farmers for land development. They also give long-term loans to farmers for acquiring new land….
Investment banks: When a corporate entity wants to issue new equity or debt securities, an investment bank serves the role of an intermediary. They sometimes also make investment in these companies through purchase of equity shares. …
Merchant banks: A merchant bank helps a company to sell its new shares to the general public. The main job of a merchant bank is raise money to lend to industry. They do not lend money themselves but instead help circulate money from those who want to lend to firms who wish to borrow….
Foreign banks:There are many foreign banks in India like the Citi Bank, the Hong Kong and Shanghai Bank and the Bank of America. These are not nationalized institutions like Indian commercial banks. …
Central bank:The central bank is the bankers’ bank and is also the banker to the government. It controls the entire banking system of the country. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is India’s central bank and the Bank of England is that of England.….
Reserve Bank of India Origin, Nationalization and structure of RBI, Monetary policy, Currency in India, Banker to the Banks, Banker to the Governments; Ways and Means advances, LORL, other related concepts.
Banking Business [Part-1]: Major Functions of Banks; Types of Deposits and Accounts; Account Operation in Banks; Individual, joint, minor, women, HUF accounts; NRI Accounts; Deposit Insurance; Bancassurance; Lending policy of the commercial banks; Major safety issues banks need to consider in lending policy.
Banking Business [Part-2]: Credit Creation; Different types of credits; Types of Loans; General modes for securing advances; NPAs; Priority Sector Lending.
Debit Card, Credit Card and Micro-Credit: History of Credit Cards; Key facts about Credit Card and Debit Card; Differences between Debit Card and Credit Card; Major players in the Credit Card transactions; Types of Cards; Size, Number of Cards; National Payments Corporation of India’s (NPCI); Credit Card Business; Kisan Credit Card Scheme; Micro Finance Development Fund.
Negotiable Instruments: Definition of NI; Cheque, Draft; Promissory Notes; bill of exchange; Crossing; Endorsing and other related concepts’ CTS-2010.
Global Banking Regulatory Framework & Basel-III: Common objectives of Banking Regulation; General Principles of Banking Regulation; Basel-I; Basel-II; Basel-III; Capital Adequacy; Capital to Risk (Weighted) Assets Ratio (CRAR); Tier-1 and Tier-2 Capital; Three pillars of Basel-III; Common Equity; Key differences between Base-II and Basel-III; Risk weighted assets; Asset Liability mismatch.
Money Markets in India: Segments of money markets in India; Various instruments of Money Markets; Call Money, Notice Money and Term Money Markets; Commercial Bills; Certificate Of Deposits (CDs); Commercial Paper (CP); Money Market Mutual Funds (MMMFs); Repo and Reverse Repo auctions; Discount And Finance House of India (DFHI); Various problems of Money Markets in India ; Salient features of Indian Money Market ; Main functions of Money Markets; Money supply & Total Stock of Money; Narrow Money, Broad Money, Reserve Money.
Capital Markets of India [Part-1]: Types of companies in India; Limited Companies; Concept of Shareholding; Different Types of Share Capital; Capital Reserves versus Reserve Capital; Types of Shares; Equity Shares; Preference Shares; Process of issuing shares; Prospectus, IPO, Red Herring Prospectus; FPO; Stock Markets.
Capital Markets [Part-2]: Debt Market, Debt Instruments-Debentures; G-secs.
Derivatives, Investments and Futures: Different Types of Derivatives; Long Term & Short term Investment Options; Spot contract; Non-Deliverable Forward; Option Premium; Commodity Future Market in India; Investments.
Non-Banking Financial Companies: Definition of NBFC; Regulation of NBFCs; Difference between NBFC and Banks; Investment Company (IC); Loan Companies (LC); Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC); Systemically Important Core Investment Company (CIC-ND-SI); Infrastructure Debt Fund (IDF-NBFC); Non-Banking Financial Company -Micro Finance Institution (NBFC-MFI); Asset Finance Company(AFC); Non-Banking Financial Company – Factors (NBFC-Factors); Residuary Non-Banking Company; Do Multi-Level Marketing companies, Chit funds etc.
Insurance Industry in India: History of Life Insurance; Life Insurance; General Insurance; IRDA; Insurance Ombudsman; Integrated Grievance Management System; Insurance Repository; Privatization of Life Insurance in India; Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Policy in Insurance Sector; Types of Life Insurance; Health Insurance In India; Employee’s State Insurance Corporation; Future of Insurance Sector; Select Terms related to Insurance Sector.
Glossary of Important Terms: Important terms and concepts related to Finance, Business and Economy sector.
In various competitive examinations candidates usually get questions on banking awareness along with general awareness section.
Banking part in examinations has the questions related to the History of Banking, banking terms, Marketing of Banking Products, Functions of Banks, Banks and their taglines, schemes, committees related to banking, headquarters of bank, some Banking news related, apps launched by banks, new schemes etc.
FEW QUESTIONS FROM BANKING AWARENESS
Q1.How many digits will be used to represent Universal Account Number?
- 10
- 11
- 20
- 12
- 15
Answer – 4. (12)
Q2. Mobile Money Identifier (MMID) is a 7 digit unique number issued by the bank. What are the last three digits represent?
- to identify the account of the user
- to identify the branch of the user
- to identify the bank of the user
- To identify the village of user
- None of these
Answer – 1. (to identify the account of the user)
Q3.PAN card will be issued under Section __________ of the Income Tax Act.
- 139A
- 189A
- 89A
- 122A
- None of these
Answer – 1. (139A)
Q4. Permanent Account Number (PAN) is used to identify the Indian nationals and regular Income Tax payer under the______________.
- Indian Income Tax Act, 1981
- Indian Income Tax Act, 1961
- Indian Income Tax Act, 1971
- None of these
Answer – 2. Indian Income Tax Act, 1961
Q5.How many digis in BSR(Basic Statistical Returns) code?
- 9
- 10
- 11
- None of these
Answer – 4. None of these , BSR is 7 digit code
Q6. Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) is 8 to 11 __________.
- digit code
- Alphabetic code
- Alpha numeric code
- None of these
Answer – 2. Alphabetic code
Q7. What does the last character represent in PAN CARD?
- type of holder
- Surname of holder
- Check digit
- None of these
Answer – 3. Check digit
Q8. International Securities Identification Number (ISIN) is a 12 alphanumeric code. What do the first two characters represent?
- Branch code
- Country code
- State code
- City code
Answer – 2.
Q9. Country codeLegal Entity Identifier (LEI) is a ____________ alpha numeric code.
1. 10
2. 11
3. 20
4. 9
Answer – 3. 20
Q10. IFS Code is 11 alpha numeric code. What is the fifth character?
- An alphabet
- Check digit
- 0
- None of these
Answer – 3. 0
