Mensuration-IBPS-PO
Mensuration
Mensuration is a part of Geometry. Mensuration basically deals with Length, Area, and Volume of different kind of shapes (Both 2D and 3D). It is a formula based and Technic oriented topic. There are different formulas for different areas and parameters. To get the desired results we need to put the values in these Mensuration formulas. Mensuration is topic of heavy calculations so it is very crucial that we must use smart strategy and methods for these calculations.
So to move ahead in the introduction to Mensuration, first we will discuss what are 2D and 3D shapes and the difference between them.
Mensuration is the skill of measuring the length of line , area of surfaces, and volume of solids from simple data of lines, points and angles. Mensuration means measuring. We use mensuration to measure the geometrical figures, to determine physical quantities such as perimeter, area, volume or length.
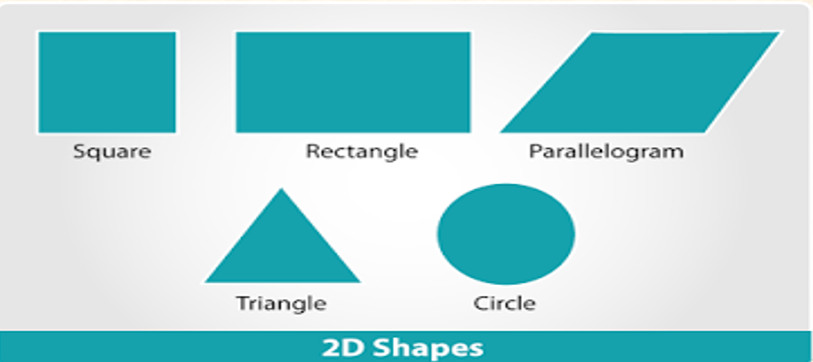
What is a 2D Shape
A 2D shape is a shape that is bounded by three or more straight lines or a closed circular line in a plane. These shapes have no depth or height; they have two dimensions- length and breadth and are therefore called 2D figures or shapes. For 2D shapes, we measure area (A) and perimeter (P).
Important terms used in Mensuration
Some important terms that constitutes these mensuration formulas.
Perimeter :
Perimeter is that measure of line which surrounds the area or shape. This is measured in meter(m), centimeter(cm) etc.
Area:
Area is a quantity that expresses the extent of a two dimensional surface or shape in the plane. It can be understood from the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat. This is measured in square units, like square meter, square centimeter etc
Volume :
Volume is the amount of space enclosed by a shape in space or say 3-D, i.e in three dimensional space with length, breath and height. This is measured in cube units, like m3 and cm3
1. Triangles: A triangle is a polygon having three sides and three angles.
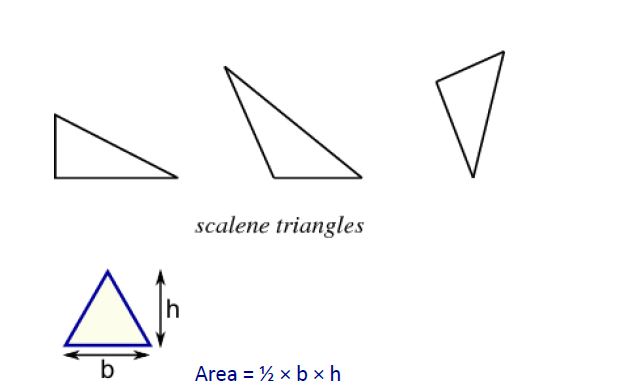
i. Sum of the angles of a triangle is 180°.
Where b = base and h = vertical height
Perimeter is sum of three sides.
The sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side.
Area = Base x Height. = x b x h
Area of a triangle ={s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}
where a, b, c are the sides of the triangle and s = (a + b + c).
ii. Pythagoras Theorem:
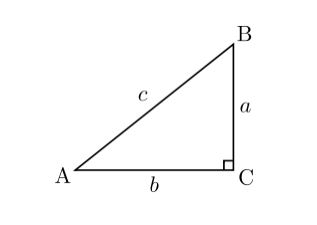
In a right-angled triangle,
(Hypotenuse)2= Base2 + Height2
In above diagram angle C is right angle i.e 90°
(AB)2 = AC2 + BC 2
c2 = a2 + b 2
iii. The line joining the mid-point of a side of a triangle to the positive vertex is called the median.
iv. The point where the three medians of a triangle meet, is called centroid. The centroid divided each of the medians in the ratio 2 : 1.
V. In an isosceles triangle, the altitude from the vertex bisects the base.
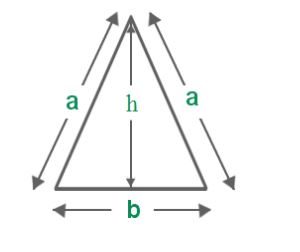
Perimeter = a + a + b = 2a + b
Area = 1/2 x Base x Height. =(1/2)(b x h)
Here h2 = a2 – (b/2)2
vi. The median of a triangle divides it into two triangles of the same area.
vii. The area of the triangle formed by joining the mid-points of the sides of a given triangle is one-fourth of the area of the given triangle.
Equilateral triangle
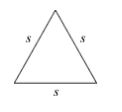
Three sides are equal and three angles are equal. If s is the side of an equilateral triangle then Perimeter = 3 s
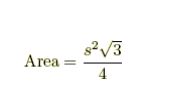
Quadrilaterals:
Quadrilateral is a four-sided figure. May be a rectangle, Square, Parallelogram, a Rhombus or a trapezium.
Rectangle
A rectangle is a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal.
If two opposite sides of a rectangle are w and h then perimeter Perimeter of a rectangle = 2(Length + Breadth) = 2(w + h)
Area of a rectangle = (Length x Breadth).
Area = w x h
And diagonals of a rectangle are equal and bisect each other.
Square:
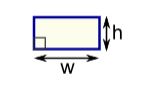
A square is a four sided figure created by connecting four line segments. All of the line segments are of the same length and they come together to form four right angles.
All four sides are equal and four angles are equal = 90 degree.
If a is each side of a square then Perimeter = 4 a
And area of a square A = a
The diagonals of a square are equal and bisect each other at right angles.
Rhombus :
A rhombus is a four-sided shape where all sides have equal length. Also opposite sides are parallel and opposite angles are equal. Another interesting thing is that the diagonals (dashed lines in second figure) meet in the middle at a right angle. In other words they “bisect” (cut in half) each other at right angles.A rhombus is a special type of parallelogram of four equal sides. The diagonals of a rhombus are unequal and bisect each other at right angles.
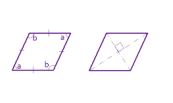
The area is the product of two adjacent sides. i.e ba
b is the length of the base
a is the altitude (height).
Another simple formula for the area of a rhombus when we know the lengths of the diagonals.
The area is half the product of the diagonals. As a formula:
Area = (d1 x d2)
Where
d1 is the length of a diagonal
d2 is the length of the other diagonal
Parallelogram :
A parallelogram is a four-sided plane rectilinear figure with opposite sides parallel.
A parallelogram and a rectangle on the same base and between the same parallels are equal in area.
Area of parallelogram = (Base x Height).
Trapezium :
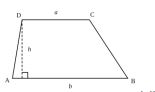
A trapezium is a quadrilateral with one pair of sides parallel.
Area of a trapezium = x (sum of parallel sides) x distance between them.
Area = h (a +b )
Area and Perimeter with examples:
Rectangular : Area = L × B
Perimeter/Circumference = 2( L + B )
Square : Area = ( side )²
Perimeter/ Circumference = 4 × side
Circle : Area = π × r²
Perimeter/ Circumference = 2 × π × r
Radius (r) = diameter/2
Diameter = r × 2
r = Radius, π = 22/7
Question 1:
The respective ratio of the length and breadth of rectangular plot is 3:2. If the length of the plot is 40 meters more than its breadth, what is the perimeter of the rectangular plot?
(1) 300 meters
(2) 400 meters
(3) 500 meters
(4) Can not be determined
(5) None of these
Answer : (2) 400 meters
Question 2:
The area of a square is three-fifth the area of a rectangular. The length of the rectangular is 25 cms. and its breadth is 10 cms less than its length. What is the perimeter of the square ?
(1) 80 cms
(2) 44 cms
(3) 60 cms
(4) 48 cms
(5) None of these
Answer : (3) 60 cms
Question 3:
The length of a rectangular is 16 cms. which is 2 cms. more than the diameter of a circle. What is the area of the circle?
(1) 112 Sq. cms.
(2) 161 Sq. cms.
(3) 160 Sq. cms.
(4) 132 Sq. cms
(5) 154 Sq. cms
Answer : (3) 154 cms
Question 4:
The area of a circular plot is twice the area of a rectangular plot. If the area of the rectangular plot is 11088 sq. meters. What is the perimeter of the circular plot?
(1) 572 meters
(2) 528 meters
(3) 440 meters
(4) 484 meters
(5) 576 meters
Answer :(2) 528 meters
Question 5:
The area of a rectangle is four-third the area of a square. The area of the square is 729 sq. cms and the length of the rectangle is 81 cms. What is the difference between the side of the square and the breadth of the rectangle ?
(1) 15 cms.
(2) 18 cms.
(3) 27 cms.
(4) 24 cms.
(5) None of these
Answer : (1) 15 cms
Question 6:
The circumference of a circle is equal to the perimeter of a rectangle. The length and the breadth of the rectangle are 45 cms. and 43 cms. respectively. What is half the radius of the circle ?
(1) 28 cms.
(2) 27 cms.
(3) 15 cms.
(4) 24 cms.
(5) None of these
Answer :(3) 15 cms
Question 7:
The area of a rectangle is 1.8 times the area of a square. The length of the rectangle is five times the breadth. The side of the square is 20 cm. What is the perimeter of the rectangle ?
(1) 145 cm
(2) 132 cm
(3) 145 cm
(4) 144 cm
(5) None of these
Answer: (4) 144 c
Question 8:
The side of a square is 5 cm. which is 13 cm, less than the diameter of a circle. What is the approximate area of the circle ?
(1) 225 sq. cm
(2) 265 sq. cm
(3) 255 sq. cm
(4) 275 sq. cm
(5) 245 sq. cm
Answer : (3) 255 sq. cm
Question 9:
The breadth of a rectangular field is 25 meters. The total cost of putting a grass bed on this field was Rs. 12,375 at the rate of Rs. 15 per meter². What is the length of the rectangular field?
(1) 37 meter
(2) 33 meter
(3) 32 meter
(4) 34 meter
(5) 30 meter
Answer : (2) 33 meter
Question 10:
The cost of putting a grass bed is Rs. 75 per sq. meter. The length of a rectangular field is 15 meter and the breadth is 4 meter less than the length. What will be the total cost of putting a grass bed on the field?
(1) Rs. 12,365
(2) Rs. 12,957
(3) Rs. 12,356
(4) Rs. 12,375
(5) None of these
Answer :(4) Rs. 12,375
Mensuration II : Volume and Surface Area
Question 1:
Find the the total surface area of cuboid whose dimensions are 25m, 10m and 2 m.
(1) 650m²
(2) 640m²
(3) 630m²
(4) 360m²
(5) None of these
Answer : (2) 640m²
Question 2:
Find the length of the longest bamboo that can be placed in a room 24 m long, 18 m broad and 16 m high.
(1) 34 m
(2) 35 m
(3) 36 m
(4) 33 m
(5) None of these
Answer : (1) 34 m
Question 3:
The area of a side of a box is 240 sq. cm. The area of the other side of the box is 72 sq. cm. If the area of the upper surface of the box is 120 sq. cm, then find the volume of the box.
(1) 1540 cm³
(2) 1440 cm³
(3) 1640 cm³
(4) 1740 cm³
(5) None of these
Answer : (2) 1440 cm³
Question 4:
The sum of length, breadth and height of a cuboid is 12 cm long. Find the total surface area of the cuboid.
(1) 70 sq. cm
(2) 90 sq. cm
(3) 80 sq. cm
(4) 60 sq. cm
(5) None of these
Answer : (3) 80 sq. cm
What is a 3D shape ?
A 3D shape is a shape that is bounded by a number of surfaces or planes. These are also referred to as solid shapes. These shapes have height or depth unlike 2D shapes; they have three dimensions- length, breadth and height/depth and are therefore called 3D figures. 3D shapes are actually made up of a number of 2D shapes. Also, know as solid shapes, for 3D shapes we measure Volume (V), Curved Surface Area (CSA), Lateral Surface Area (LSA) and Total Surface Area (TSA).
Example Figure
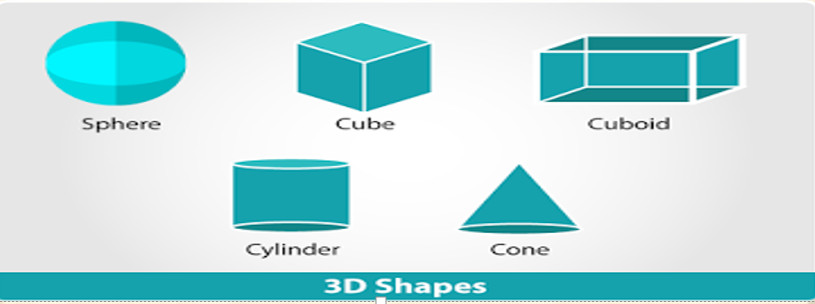
Mensuration Formulas for 3D Figures
CUBOID
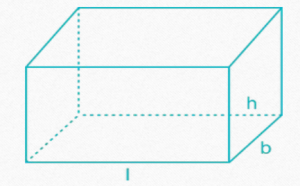
In the following formulae, l = length, b = breadth and h = height
• Total surface area of cuboid = 2 (lb + bh + lh)
• Length of diagonal of cuboid= √(++)
• Volume of cuboid = l × b × h
CUBE
In the following formulae, l = length, b = breadth and h = height
• Total surface area of cuboid = 2 (lb + bh + lh)
• Length of diagonal of cuboid= √(++)
• Volume of cuboid = l × b × h
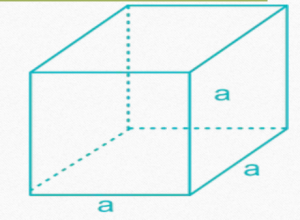
CUBE
In the following formulae, a = side of a cube
• Volume of cube =
• Total surface area of cube = 6
• Length of Leading Diagonal of Cube = a√3
CONE
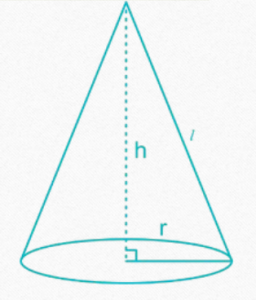
In the following formulae, r = radius of base, l = slant height of cone and h = height
of the cone (perpendicular to base)
• Slant height of a cone = l =√( + )
• Curved surface area of a cone = C = π × r × l
• Total surface area of a cone = π × r × (r + l)
• Volume of right circular cone =1/3 πr2h
CYLINDER
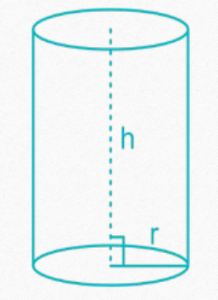
SPHERE
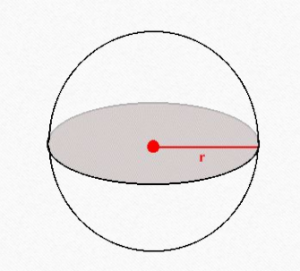
HEMISPHERE
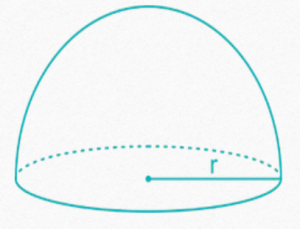
In the following formulae, r = radius of sphere
• Volume of a hemisphere =(2/3)π
• Curved surface area of a hemisphere = 2π
• Total surface area of a hemisphere = 3π
HOLLOW CYLINDER
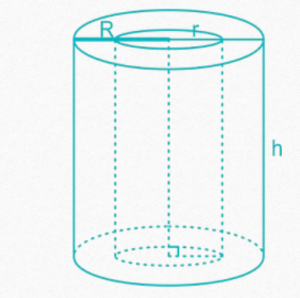
Hollow cylinder made by cutting a smaller cylinder of same height and orientation
out of a bigger cylinder.
Volume of hollow cylinder = πh(– )
(Where, R = radius of cylinder,
r = radius of cavity, h = height of cylinder)
FRUSTUM OF A RIGHT CIRCULAR CONE
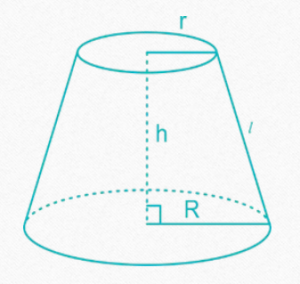
Frustum is created when a plane cuts a cone parallel to its base.In the following
formulae, R = radius of the base of the frustum, r = radius of the top of the frustum,
h = height of the frustum, l = slant height of the frustum
• If a cone is cut by a plane parallel to the base of the cone, the lower part is called
the frustum of the cone.
• Slant height of the frustum =l=√(+()
• Curved surface area of frustum = π(R + r)l
• Total surface area of frustum = π(R + r)l + π( + )
• Volume of the frustum=(1/3)πh( + +Rr)
PRISM
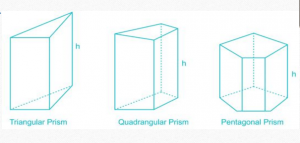
Prism consists of two polygonal bases which are parallel to each other.
These bases are joined by lateral faces, which are perpendicular to the polygonal bases.
• The number of lateral faces is equal to the number of sides in the polygonal base. Thus,
the base of a prism could be of various shapes, namely
• triangular, quadrangular, pentagonal etc.
• Volume of prism = Base area × height
• Lateral surface area of prism=perimeter of base × height
• Total surface area of prism= Lateral surface area + (2 × base area)
PYRAMID
Pyramid consists of a polygonal base and triangles at its sides. These triangles are called faces.
• The base could be of any shape, whereas the faces are generally isosceles triangles.
• All these triangular faces meet in a single point called the apex.
• Total surface area of pyramid= base area + (number of sides × ½ × slant height × base length)
• Volume of pyramid = (1/3) × base area × height
