Heredity and Evolution
HEREDITY AND EVOLUTION
In this chapter, we will study the mechanism by which variations are created and the long-term consequences of the accumulation of variations that is evolution.
Some Important Definitions
- Genetics : Branch of science that deals with Heredity and variation.
- Heredity : It means the transmission of features/ characters/ traits from one generation to the next generation.
- Variation : The differences among the individuals of a species/population are called variations.It takes place due to environment changes,crossing over,and recombination of genes and mutation.
- Genotype: The complete set of genes in an organism’s genome is called genotype.
- Phenotype: The observable characters in an organism make the phenotype. Phenotype is a modified genotype and many of the phenotypes cannot be inherited.
ACCUMULATION OF VARIATION DURING REPRODUCTION
Inheritance from the previous generation provides both a common basic body design, and subtle changes in it,
for the next generation. The second generation will have differences that they inherit from the first generation, as well as newly created differences.
Very minor differences can be seen in asexual reproduction.
In Sexual reproduction is involved, even greater diversity can be generated.
HEREDITY
It refers to the transmission of characters or traits from parents to their offspring. Heredity is the continuation of features from one generation to another which are present in fertilised egg or zygote.
Inherited Traits (Rules for the Inheritance of Traits – Mendel’s Contributions)
rules for inheritance of traits in human beings are related to the fact that both the father and the mother contribute practically equal amounts of genetic material to the child. This means that each trait can be influenced by both paternal and maternal DNA, Thus, for each trait there will be two versions in each child.
Gregor Johann Mendel (1822–1884) ,known as the father of genetics experimented on plant breeding and hybridisation.
He chose pisum sativum (pea plant ) with a number of contrasting visible characters, like- round/wrinkled seeds, tall/short plants, white/violet flowers and so on for his experiment.
He chose pea plant due to a number of following reasons-
- Availability of detectable contrasting traits of several characters.
- short life span.
- normally self fertilisation occours but cross fertilization can also be carried out.
- Large no of seeds produced.
Monohybrid Cross
It is called Monohybrid cross because only one characteristic is experimented with that is height
He took pea plants with different characteristics – a tall plant(TT) and a short plant(tt), produced progeny from them, and calculated the percentages of tall or short progeny.
There were no halfway characteristics in this first generation, or F1 progeny – no ‘medium-height’ plants. All plants were tall.

Only one of the parental traits was seen that is tallness of plants
In the second-generation, or F2, progeny of the F1 tall plants one quarter of the were short.
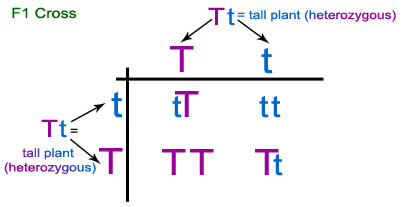

This showed that both the tallness and shortness traits were inherited in the F1 plants, but only the tallness trait was expressed.
In this explanation, both TT and Tt are tall plants, while only tt is a short plant .
Thus a single copy of ‘T’ is enough to make the plant tall, while both copies have to be ‘t’ for the plant to be short. Traits like ‘T’ are called dominant traits, while those that behave like ‘t’ are called recessive traits.
DIHYBRID CROSS
Two different characteristics together is experimented with.
It is simply a cross between two plants having two pairs of contrasting characters is Dihybrid cross.
For Example a plant with round(RR) and yellow(YY) seeds and a plant with wrinkled (rr) and green (yy)seeds crossed together.

Inherited Traits-How do these Traits get Expressed
- Cellular DNA is the information source for making proteins in the cell.
- A section of that DNA provides information for one protein called gene.
- genes control characteristics, or traits
Sex Determination
Determination of sex of an offspring is called sex determination.
Environmental and Genetic Factors are responsible for sex determination.
Environmental-in some animals, the temperature at which fertilised eggs are kept determines whether the animals developing in the eggs will be male or female.
Genetic- in some case , sex of the individual is largely genetically determined by a pair of chromosomes called sex chromosome.
XX- Female Chromosome
XY-Male chromosome
sex chromosome
In human there are 23 pairs of chromosome. Out of these 22 chromosomes pairs are called autosomes and the last pair of chromosome that help in deciding gender of that individual is called sex chromosome.
Women have a perfect pair of sex chromosomes, both called X.
Men have a mismatched pair in which one is a normal-sized X while the other is a short one called Y.

- Thus half the children will be boys and half will be girls.
- All children will inherit an X chromosome from their mother regardless of whether they are boys or girls.
- Thus sex of the children will be determined by what they inherit from their father. One who inherits an X chromosome from her father will be a girl, and one who inherits a Y chromosome from him will be a boy.
EVOLUTION
Evolution is the sequence of gradual changes which takes place in the primitive organisms, over millions of years, in which new species are produced.
Since genes control traits, we can say that the frequency of certain genes in a population changed over generations. This is the essence of the idea of evolution.
Acquired and Inherited Traits
Acquired Traits are the traits that are developed in an individual due to some special conditions.
These are not inherited over generations.
These do not lead to evolution.
Inherited Traits are traits that is passed on throughout generations.
These trait help in evolution.
SPECIATION
Micro Evolution : It is the evolution which is on a small scale.
Speciation : it is the process of formation of new species from the existing species.
Species : A group of similar individuals within a population that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
Factors which lead to speciation : Geographical isolation,genetic drifts and variations.
Geneflow : It is exchange of genetic material by interbreeding between populations of same species or individuals.
Genetic Drift :It is the random change in the frequency of alleles (gene pair) in a population over successive generations. Genetic Drift takes place due to severe changes in DNA change in number of chromosomes.
Natural Selection : The process by which nature selects and consolidate those organisms which are more suitably adapted and possesses favorable variations.
Geographical Isolation :It is caused by Mountain Ranges , Rivers etc, Which leads to reproductive Isolation So there is no flow of genes between separated population.
EVOLUTION AND CLASSIFICATION
Evolution is the process by which different kinds of living organism are believed to have developed from earlier forms during the history of the earth
Both evolution and classification are interlinked.
1. Classification of species is reflection of their evolutionary relationship.
2. The more characteristic two species have in common the more closely they are related.
3. The more closely they are related, the more recently they have a common ancestor.
4. Similarities among organisms allow us to group them together and to study their characteristic.
TRACING EVOLUTIONARY RELATIONSHIPS
Jean Baptiste Lamarck gave the first theory of evolution. The accepted one is The Origin of Species by Charles Darwin.
Evidences of Evolution
Homologous Organs : Morphological and anatomical evidences. These are the organs that have same basic structural plan and origin but different functions.
Homologous organs provides evidence for evolution by telling us that they are derived from the same ancestor.
As an example mammals have four limbs, as do birds, reptiles and amphibians. The basic structure of the limbs
is similar though it has been modified to perform different functions in various vertebrates.
Analogous Organs : These are the organs that have different origin and structural plan but same function .
For example wings of bat and bird, The designs of the two wings, their structure and components, are thus very different. They look similar because they have a common use for flying, but their origins are not common. This makes them analogous characteristics.
Fossils
Preserved traces of living organisms are called fossils. They help in studies of organ structure.
Evolution By Stages
Complex organs may have evolved because of the survival advantage of even the
intermediate stages.
Organs or features may be adapted to new functions during the course of evolution.
For example, feathers are thought to have been initially evolved for warmth and
later adapted for flight.
Evolution cannot be said to ‘progress’ from ‘lower’ forms to ‘higher’ forms. Rather,
evolution seems to have given rise to more complex body designs even while the
simpler body designs continue to flourish.
Human Evolution
Study of the evolution of human beings indicates that all of us belong to a single
species that evolved in Africa and spread across the world in stages.1. Which of the following is totally impossible outcome of Mendel Experiment?
a. 3 tall 1 short plant
b. 24 tall and 8 short plants
c. 8 tall and 0 short plants
d. 4 tall plants and 1 medium height plant.
Answer -d
2. Which of the following is not a direct conclusion that can be drawn from Mendel Experiment?
a. Only one parental trait is expressed
b. Natural selection can alter frequency of an inherited trait.
c. For recessive trait to be expressed, both copies should be identical
d. Two copies of each trait is inherited in sexually reproducing organism
Answer -b
3. Which section of DNA provides information for one protein
a. Nucleus
b. Chromosomes
c. Trait
d. Gene
Answer -d
4. What is the probability that the male progeny will be a boy?
a. 50%
b. 56%
c. 47.43%
d. It varies
Answer -a5. Who have a perfect pair of sex chromosomes? a. Girls only b. Boys only c. Both girls and boys d. It depends on many other factors Answer -a 6. With whom you can associate theory of evolution? a. Charles Darwin b. Mendel c. Stanley miller d. Harold Urey Answer -a 7. Which of the following can be called a characteristic? a. Plants can photosynthesis b. We have 2 eyes c. Mango tree is multicellular d. All of these Answer -d 8. Homologous organ have a. Same structure, same function b. Different structure, different function c. Same structure, different function d. different structure, same function Answer -c
